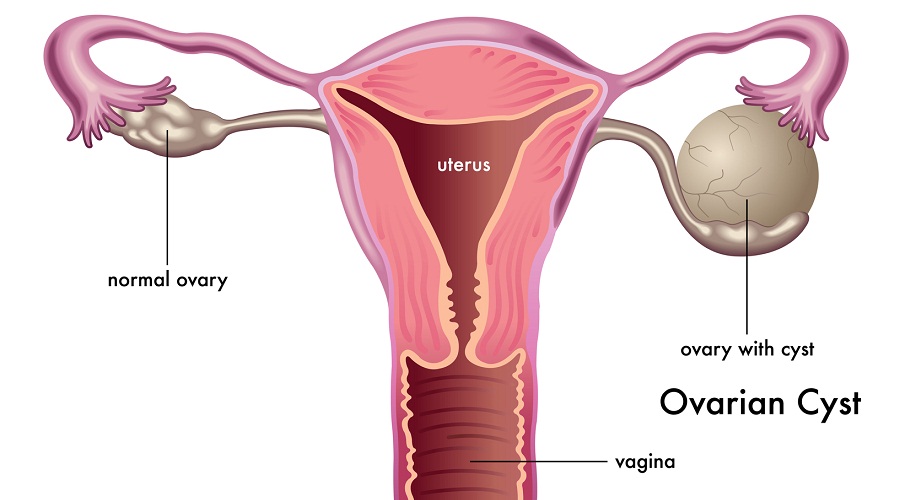
Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs or pockets in an ovary or on its surface. Women have two ovaries — each about the size and shape of an almond — on each side of the uterus. Eggs (ova), which develop and mature in the ovaries, are released in monthly cycles during the childbearing years.
Many women have ovarian cysts at some time. Most ovarian cysts present little or no discomfort and are harmless. The majority disappears without treatment within a few months.
However, ovarian cysts — especially those that have ruptured — can cause serious symptoms. To protect your health, get regular pelvic exams and know the symptoms that can signal a potentially serious problem.
Symptoms
Most cysts don't cause symptoms and go away on their own. However, a large ovarian cyst can cause:
- Pelvic pain — a dull or sharp ache in the lower abdomen on the side of the cyst
- Fullness or heaviness in your abdomen
- Bloating
When to see a doctor
Seek immediate medical attention if you have:
- Sudden, severe abdominal or pelvic pain
- Pain with fever or vomiting
If you have these signs and symptoms or those of shock — cold, clammy skin; rapid breathing; and lightheadedness or weakness — see a doctor right away.
Causes
Most ovarian cysts develop as a result of your menstrual cycle (functional cysts). Other types of cysts are much less common.
Functional cysts
Your ovaries normally grow cyst-like structures called follicles each month. Follicles produce the hormones estrogen and progesterone and release an egg when you ovulate.
If a normal monthly follicle keeps growing, it's known as a functional cyst. There are two types of functional cysts:
- Follicular cyst. Around the midpoint of your menstrual cycle, an egg bursts out of its follicle and travels down the fallopian tube. A follicular cyst begins when the follicle doesn't rupture or release its egg, but continues to grow.
- Corpus luteum cyst. When a follicle releases its egg, it begins producing estrogen and progesterone for conception. This follicle is now called the corpus luteum. Sometimes, fluid accumulates inside the follicle, causing the corpus luteum to grow into a cyst.
Functional cysts are usually harmless, rarely cause pain, and often disappear on their own within two or three menstrual cycles.
Other cysts
Types of cysts not related to the normal function of your menstrual cycle include:
- Dermoid cysts. Also called teratomas, these can contain tissue, such as hair, skin or teeth, because they form from embryonic cells. They're rarely cancerous.
- Cystadenomas. These develop on the surface of an ovary and might be filled with a watery or a mucous material.
- Endometriomas. These develop as a result of a condition in which uterine endometrial cells grow outside your uterus (endometriosis). Some of the tissue can attach to your ovary and form a growth.
Diagnosis
A cyst on your ovary can be found during a pelvic exam. Depending on its size and whether it's fluid filled, solid or mixed, your doctor likely will recommend tests to determine its type and whether you need treatment. Possible tests include:
- Pregnancy test. A positive test might suggest that you have a corpus luteum cyst.
- Pelvic ultrasound. A wandlike device (transducer) sends and receives high-frequency sound waves (ultrasound) to create an image of your uterus and ovaries on a video screen. Your doctor analyzes the image to confirm the presence of a cyst, help identify its location and determine whether it's solid, filled with fluid or mixed.
- Laparoscopy. Using a laparoscope — a slim, lighted instrument inserted into your abdomen through a small incision — your doctor can see your ovaries and remove the ovarian cyst. This is a surgical procedure that requires anesthesia.
- CA 125 blood test. Blood levels of a protein called cancer antigen 125 (CA 125) often are elevated in women with ovarian cancer. If your cyst is partially solid and you're at high risk of ovarian cancer, your doctor might order this test.
Elevated CA 125 levels can also occur in noncancerous conditions, such as endometriosis, uterine fibroids and pelvic inflammatory disease.